The question “is hydrogen sulfide polar” seeks to understand the polarity of the hydrogen sulfide molecule. We can rephrase it as: “Does hydrogen sulfide exhibit polarity, and what factors determine its polar or non - polar nature?”
Is Hydrogen Sulfide Polar? Exploring the Molecular Polarity
Related Encyclopedia
Related Products More >
-
- 7757-93-11
- CNY equest For Quotation
-
- 7757-93-10
- CNY equest For Quotation
-
- 7757-93-9
- CNY equest For Quotation
-
- 92128-87-5
- CNY equest For Quotation
-
- 92128-87-5
- CNY equest For Quotation
-
- 13472-35-0
- USD 22.0000
- 25kg
-
- 13530-50-2
- USD 240.0000
- 300kg
-
- 13530-50-2
- USD 45.0000
- 25kg


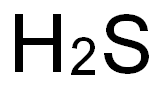


 沪ICP备2021018848号-5
沪ICP备2021018848号-5

Sulfur (S) has an electronegativity of about 2.58, while hydrogen (H) has an electronegativity of about 2.20. The electronegativity difference between sulfur and hydrogen is (2.58 - 2.20=0.38).
This difference causes the shared electrons in the H - S bonds to be pulled more towards the sulfur atom, creating a partial negative charge delta on the sulfur and partial positive charges (delta+) on the hydrogen atoms.
Molecular Geometry: The molecular geometry of H2S is bent or V - shaped. The sulfur atom has two bonding pairs (with hydrogen atoms) and two lone pairs of electrons. The lone pairs exert a greater repulsive force than the bonding pairs, causing the H - S - H bond angle to be approximately 92^circ).
This non - linear shape, combined with the polar H - S bonds, results in an overall dipole moment for the molecule, making it polar.Case Study: Hydrogen Sulfide in the Oil and Gas IndustryIn the oil and gas industry, hydrogen sulfide is a common by - product.
It is often present in natural gas and crude oil. The polarity of hydrogen sulfide allows it to dissolve in water to some extent. When water is present in the extraction and processing equipment, hydrogen sulfide can dissolve in it and form an acidic solution. This acidic solution can cause corrosion of metal pipes and equipment.
For example, in a natural gas processing plant, if hydrogen sulfide is not properly removed, it can lead to the degradation of pipelines over time, increasing the risk of leaks and safety hazards.
Operational Considerations and SafetyDetection: Since hydrogen sulfide is a toxic and odorless gas at high concentrations (although it has a characteristic “rotten egg” smell at low concentrations), proper detection equipment should be used in areas where it may be present.Ventilation: Ensure good ventilation in work areas to prevent the accumulation of hydrogen sulfide.
This is especially important in confined spaces.Personal Protective Equipment (PPE): Workers should wear appropriate PPE, such as gas masks with hydrogen sulfide filters, when working in environments where there is a risk of exposure.Removal Processes: Implement effective removal processes for hydrogen sulfide in industrial settings. For example, chemical scrubbers can be used to react with and remove hydrogen sulfide from gas streams.
Hydrogen sulfide consists of two hydrogen atoms bonded to a sulfur atom. Sulfur is more electronegative than hydrogen, meaning it pulls the shared electrons closer to itself. This creates a difference in charge, with the sulfur side being slightly negative and the hydrogen side being slightly positive.
In addition to the difference in electronegativity, the shape of the H₂S molecule is important. H₂S has a bent (or V-shaped) molecular structure due to the two lone pairs of electrons on the sulfur atom. These lone pairs push the hydrogen atoms down, creating an angle between the bonds. This bent shape prevents the dipoles from canceling each other out, making the overall molecule polar.
If H₂S were a linear molecule, the individual bond dipoles could cancel, and the molecule would be nonpolar. But because it is bent, the molecule has an uneven distribution of charge, resulting in a net dipole moment.
In summary, hydrogen sulfide is polar because it has polar bonds and a bent molecular shape that causes an uneven distribution of electrical charge.
Explanation: Why is Hydrogen Sulfide Polar?
To understand the polarity of hydrogen sulfide, we must first examine its molecular structure. Hydrogen sulfide consists of two hydrogen atoms bonded to one sulfur atom. The electronegativity values of the elements involved are as follows:
Hydrogen (H): 2.20
Sulfur (S): 2.58
The difference in electronegativity between hydrogen and sulfur (0.38) is less than the typical threshold of 0.4 for a polar covalent bond, but it is still significant enough to result in a polar molecule. In H₂S, the sulfur atom is more electronegative than the hydrogen atoms, leading to an unequal sharing of electrons. This creates a dipole moment, where the sulfur end of the molecule is partially negative (δ⁻) and the hydrogen ends are partially positive (δ⁺).
The bent shape of the H₂S molecule further enhances its polarity. Unlike linear molecules, where the dipole moments may cancel out, the bent geometry of H₂S (approximately 92 degrees) means that the dipole moments do not cancel, resulting in an overall net dipole moment for the molecule. Thus, hydrogen sulfide is classified as a polar molecule.
Case Study: The Role of Hydrogen Sulfide in Life and Industry
In Nature
Hydrogen sulfide is a naturally occurring gas that is often associated with volcanic activity and the decomposition of organic matter, particularly in environments devoid of oxygen. It is also produced by certain bacteria in the absence of oxygen, a process known as anaerobic digestion. In marine environments, hydrogen sulfide can be found in deep-sea hydrothermal vents, where it supports unique ecosystems of organisms that thrive in extreme conditions.
In the Chemical Industry
Industrially, hydrogen sulfide is a significant compound with various applications. It is used in the production of sulfur and sulfuric acid, which are essential in many chemical processes. Additionally, H₂S is a byproduct of many industrial processes, including the refinement of petroleum and natural gas. The management of hydrogen sulfide is crucial, as it is toxic and can pose health risks at high concentrations.
In the oil and gas industry, for example, hydrogen sulfide is often encountered during the extraction and processing of crude oil and natural gas. It is essential to monitor and mitigate H₂S levels to ensure the safety of workers and the environment. Technologies such as gas scrubbing and absorption are employed to remove hydrogen sulfide from gas streams, converting it into elemental sulfur through processes like the Claus process.
Precautions During Operation or Use
When handling hydrogen sulfide, several precautions must be taken to ensure safety:
Ventilation: Ensure adequate ventilation in areas where hydrogen sulfide may be present to prevent the accumulation of the gas, which can lead to dangerous levels of exposure.
Monitoring: Use gas detectors to monitor H₂S levels in the workplace. This is crucial for early detection and response to potential leaks or releases.
Personal Protective Equipment (PPE): Workers should wear appropriate PPE, including respirators, gloves, and protective clothing, to minimize exposure to hydrogen sulfide.
Training: Proper training should be provided to all personnel working with or around hydrogen sulfide. Understanding the risks and proper response protocols is essential for safety.
Emergency Procedures: Establish and communicate clear emergency procedures for dealing with hydrogen sulfide leaks or exposure. This includes evacuation plans and first aid measures.