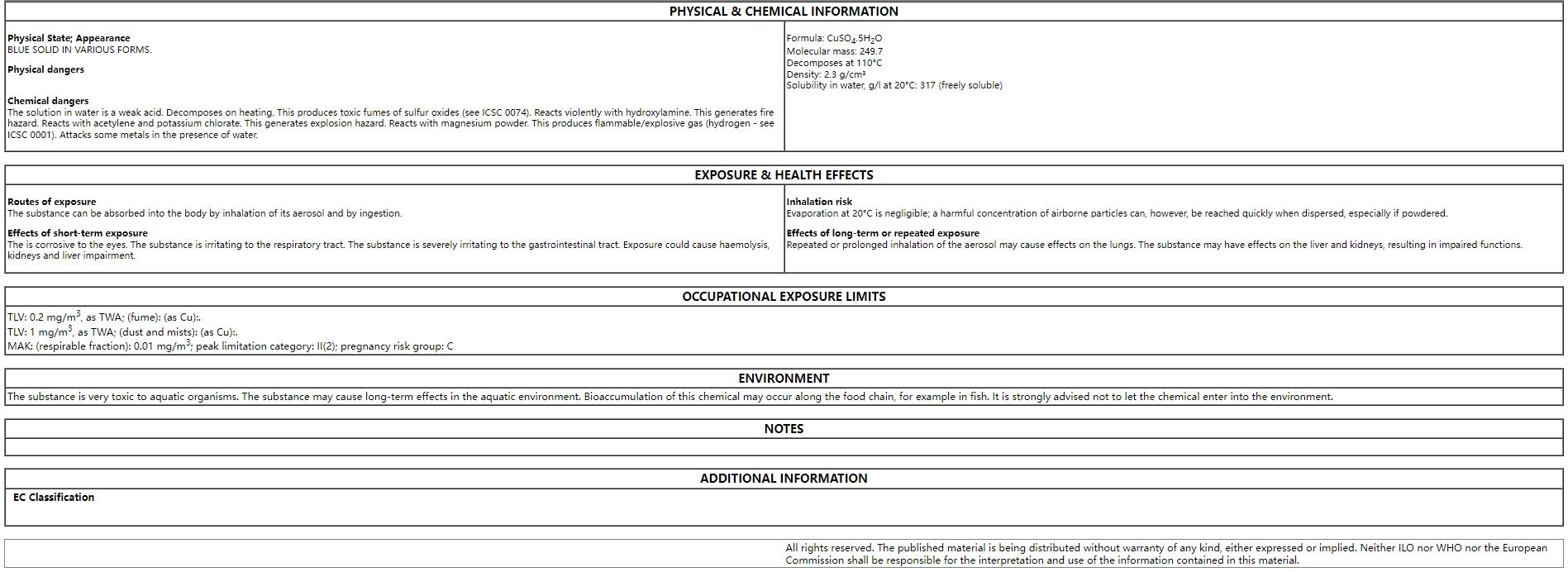
FCC Copper Sulfate Pentahydrate CuSO4 5H2O CAS 7758-99-8 CuSO4 Copper (II) Sulfate Pentahydrate Electroplating
 Unit 801, Building2, Xinglinwan Road, Jimei District, XIAMEN,CHINA
Unit 801, Building2, Xinglinwan Road, Jimei District, XIAMEN,CHINA Send me a request
Send me a request
Product Details & Description
Product Info
Chemical Identifiers
Product Info
1、Chemical Name: Copper (II) Sulfate Pentahydrate
2、Molecular Formula: CuSO4·5H2O
3、Molecular Mass: 249.7g/mol
4、CAS: 7758-98-7
5、Character: It’s dark blue triclinic crystal or blue crystalline powder or granule. It smells like nasty metal. It effloresces slowly in dry air. Relative density is 2.284. When above 150℃, it loses water and form Anhydrous Copper Sulfate which absorbs water easily. It’s soluble in water freely and aqueous solution is acidic. PH value of 0.1mol/L aqueous solution is 4.17(15℃). It’s soluble in glycerol freely and dilute ethanol but insoluble in pure ethanol.
6、Usage: It is used as nutritional supplement, antimicrobial agent, firming agent and processing aid.
7、Packing: It is packed with polyethylene bag as inner layer, and a compound plastic woven bag as outer layer. The net weight of each bag is 25kg.
8、Storage and Transport: It should be stored in a dry and ventilative warehouse, kept away from heat and moisture during transportation, unloaded with care so as to avoid damage. Furthermore, it must be stored separately from poisonous substances.
CAS No.
7758-99-8
Purity
96%, 98%
Other Attributes
Type
Copper Sulphate
Place of Origin
Shandong, China
Classification
Sulphate
Other Names
Copper Sulfate, Blue Vitriol
MF
CuSO4.5H2O
EINECS No.
231-847-6
Grade Standard
Agriculture Grade, Industrial Grade
Appearance
Blue Crystal
Application
Electroplating, Mineral Processing
Color
Blue
HS
28332500.10
Cu
25%min
Crystal Size
20~30mesh
Granular Size
2~4mm
Relative Density
2.28
CuSO4.5H2O
90%~98%
Melting Point
160℃
Relative Molecular Weight
249.68
Solubility
32g (20℃)
Packaging and Delivery
Packaging Details
1.Packed in plastic-lined woven bags of 25Kg net each, 27MT per 20FCL.
2.Packed in plastic-lined woven jumbo bags of 1250Kg net each, 25MT per 20FCL.
3.According to the customer's requirement.
Port
Qingdao, Tianjin
Selling Units:
Single item
Single package size:
20X10X75 cm
Single gross weight:
25.100 kg
Supply Ability
Supply Ability
5000 Ton/Tons per Month
Copper (II) Sulfate Pentahydrate
SpecificationGB29210-2012FCC VIIContent (CuSO4·5H2O), w/%98.0-102.098.0-102.0Substances Not Precipitated by Hydrogen Sulfide,w/%≤0.30.3Iron (Fe), w/% ≤0.010.01Lead (Pb),mg/kg ≤44Arsenic (As),mg/kg ≤3————
Toxicological effects

Analytical reagent
Several chemical tests utilize copper sulfate. It is used in Fehling's solution and Benedict's solution to test for reducing sugars, which reduce the soluble blue copper(II) sulfate to insoluble red copper(I) oxide. Copper(II) sulfate is also used in the Biuret reagent to test for proteins.
Copper sulfate is used to test blood for anemia. The blood is dropped into a solution of copper sulfate of known specific gravity—blood with sufficient hemoglobin sinks rapidly due to its density, whereas blood which sinks slowly or not at all has an insufficient amount of hemoglobin. Clinically relevant, however, modern laboratories utilize automated blood analyzers for accurate quantitative hemoglobin determinations, as opposed to older qualitative means.
In a flame test, the copper ions of copper sulfate emit a deep green light, a much deeper green than the flame test for barium.
Organic synthesis
Copper sulfate is employed at a limited level in organic synthesis. The anhydrous salt is used as a dehydrating agent for forming and manipulating acetal groups. The hydrated salt can be intimately mingled with potassium permanganate to give an oxidant for the conversion of primary alcohols.
Rayon production
Reaction with ammonium hydroxide yields tetraamminecopper(II) sulfate or Schweizer's reagent which was used to dissolve cellulose in the industrial production of Rayon.
Niche uses
Copper(II) sulfate has attracted many niche applications over the centuries. In industry copper sulfate has multiple applications. In printing it is an additive to book-binding pastes and glues to protect paper from insect bites; in building it is used as an additive to concrete to improve water resistance and discourage anything from growing on it. Copper sulfate can be used as a coloring ingredient in artworks, especially glasses and potteries. [32] Copper sulfate is also used in firework manufacture as a blue coloring agent, but it is not safe to mix copper sulfate with chlorates when mixing firework powders.
Lowering a copper etching plate into the copper sulfate solution
Copper sulfate was once used to kill bromeliads, which serve as mosquito breeding sites. Copper sulfate is used as a molluscicide to treat bilharzia in tropical countries.
Art
In 2008, the artist Roger Hiorns filled an abandoned waterproofed council flat in London with 75,000 liters of copper(II) sulfate water solution. The solution was left to crystallize for several weeks before the flat was drained, leaving crystal-covered walls, floors and ceilings. The work is titled Seizure. Since 2011, it has been on exhibition at the Yorkshire Sculpture Park.
Etching
Copper(II) sulfate is used to etch zinc, aluminium, or copper plates for intaglio printmaking. It is also used to etch designs into copper for jewelry, such as for Champlevé.
Dyeing
Copper(II) sulfate can be used as a mordant in vegetable dyeing. It often highlights the green tints of the specific dyes.
Electronics
An aqueous solution of copper(II) sulfate is often used as the resistive element in liquid resistors.
In electronic and microelectronic industry a bath of CuSO4·5H2O and sulfuric acid (H2SO4) is often used for electrodeposition of copper.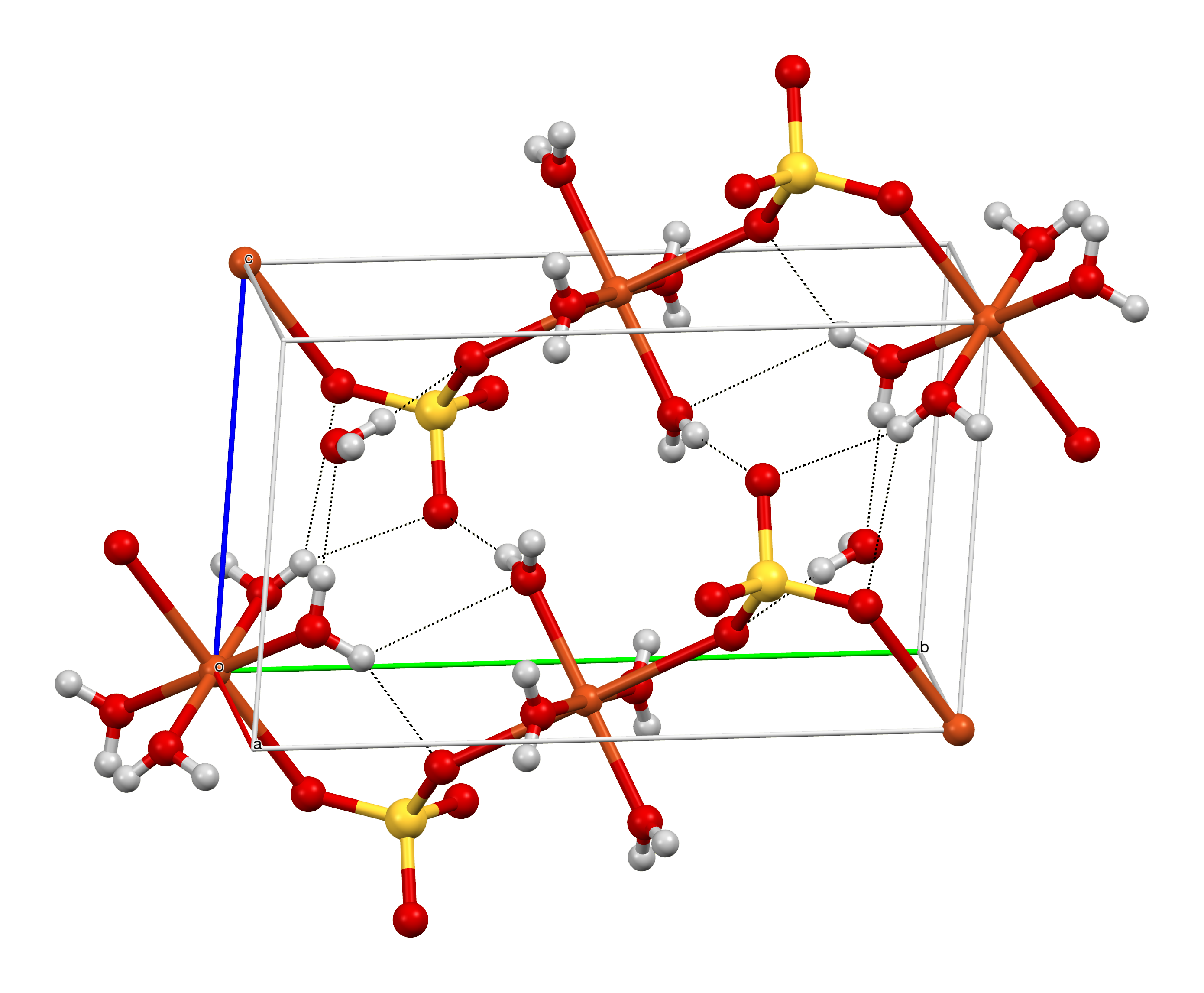
IUPAC Name
Copper(II) Sulfate
Other names
Cupric sulphate
Blue vitriol (pentahydrate)
Bluestone (pentahydrate)
Bonattite (trihydrate mineral)
Boothite (heptahydrate mineral)
Chalcanthite (pentahydrate mineral)
Chalcocyanite (mineral)
Copper Sulphate pentahydrate
IdentifiersCAS Number
7758-98-7 (anhydrous)
7758-99-8 (pentahydrate)
16448-28-5 (trihydrate)
19086-18-1 (heptahydrate)
3D model (JSmol)
Interactive image
ChEBICHEBI:23414
ChEMBLChEMBL604
ChemSpider22870
ECHA InfoCard100.028.952 EC Number231-847-6
Gmelin Reference
8294KEGGC18713
PubChem CID
24462
RTECS numberGL8800000 (anhydrous)
GL8900000 (pentahydrate)
UNIIKUW2Q3U1VV (anhydrous)
LRX7AJ16DT (pentahydrate)
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
DTXSID6034479
PropertiesChemical formula
CuSO4 (anhydrous)
CuSO4·5H2O (pentahydrate)Molar mass159.60 g/mol (anhydrous)
249.685 g/mol (pentahydrate)Appearancegray-white (anhydrous)
blue (pentahydrate)Density3.60 g/cm3 (anhydrous)
2.286 g/cm3 (pentahydrate)Melting point110 °C (230 °F; 383 K) decomposes
560 °C decomposes [2](pentahydrate)
Fully decomposes at 590 °C (anhydrous)
Boiling pointdecomposes to cupric oxide at 650 °CSolubility in water
pentahydrate
316 g/L (0 °C)
2033 g/L (100 °C)anhydrous
168 g/L (10 °C)
201 g/L (20 °C)
404 g/L (60 °C)
770 g/L (100 °C)Solubilityanhydrous
insoluble in ethanolpentahydrate
soluble in methanol
10.4 g/L (18 °C)
insoluble in ethanol and acetoneMagnetic susceptibility (χ)
1330·10−6 cm3/molRefractive index (n D)
1.724–1.739 (anhydrous)
1.514–1.544 (pentahydrate)StructureCrystal structure
Orthorhombic (anhydrous, chalcocyanite), space group Pnma, oP24, a = 0.839 nm, b = 0.669 nm, c = 0.483 nm. [6]
Triclinic (pentahydrate), space group P1, aP22, a = 0.5986 nm, b = 0.6141 nm, c = 1.0736 nm, α = 77.333°, β = 82.267°, γ = 72.567° [7]ThermochemistryStd molar
entropy (S ⦵ 298)
5 J/(K·mol)Std enthalpy of
formation (Δf H ⦵ 298)
−769.98 kJ/molPharmacologyATC code
V03AB20 ( WHO)HazardsGHS labelling:Pictograms

 NFPA 704 (fire diamond)
NFPA 704 (fire diamond)
Flash pointNon-flammableLethal dose or concentration (LD, LC):LD50 (median dose)
300 mg/kg (oral, rat)
87 mg/kg (oral, mouse)
NIOSH (US health exposure limits):PEL (Permissible)
TWA 1 mg/m3 (as Cu)REL (Recommended)
TWA 1 mg/m3 (as Cu)IDLH (Immediate danger)
TWA 100 mg/m3 (as CuSafety data sheet (SDS)anhydrous
pentahydrateRelated compoundsOther cations
Iron(II) sulfate
Manganese(II) sulfate
Nickel(II) sulfate
Zinc sulfate


 沪ICP备2021018848号-5
沪ICP备2021018848号-5
