The query “c7h16 consti isomers” asks about the number and structures of constitutional isomers (compounds with the same molecular formula but different connectivity of atoms) for heptane (C₇H₁₆). Reframed, the question becomes: How many constitutional isomers exist for the molecular formula C₇H₁₆, and what principles govern their structural diversity?
How Many Constitutional Isomers Does C₇H₁₆ (Heptane) Have? A Structural Analysis
Related Encyclopedia
Related Products More >
-
- USD 30.0000
- 6kg
-
- CNY equest For Quotation
-
- CNY equest For Quotation
-
- CNY equest For Quotation
-
- CNY equest For Quotation
-
- CNY equest For Quotation
-
- CNY equest For Quotation
-
- CNY equest For Quotation


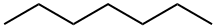

 沪ICP备2021018848号-5
沪ICP备2021018848号-5

Heptane (C₇H₁₆) has 9 distinct constitutional isomers. These arise from varying degrees of carbon chain branching, leading to different structural arrangements while maintaining the same number of carbon and hydrogen atoms.
Structural Breakdown of Isomers
Constitutional isomers of C₇H₁₆ are categorized by the length of the parent carbon chain and the position of alkyl substituents (e.g., methyl, ethyl groups). The isomers are:
n-Heptane (straight chain, no branching).
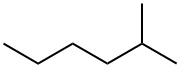
2-Methylhexane (one methyl group on the 2nd carbon).
3-Methylhexane (one methyl group on the 3rd carbon).
2,2-Dimethylpentane (two methyl groups on the 2nd carbon).
2,3-Dimethylpentane (methyl groups on the 2nd and 3rd carbons).
2,4-Dimethylpentane (methyl groups on the 2nd and 4th carbons).
3,3-Dimethylpentane (two methyl groups on the 3rd carbon).
3-Ethylpentane (one ethyl group on the 3rd carbon).
2,2,3-Trimethylbutane (three methyl groups on the 2nd and 3rd carbons).
Why Branching Creates Isomers
Carbon’s Tetravalency: Carbon atoms can form four covalent bonds, allowing for branching when forming alkanes.
Isomer Count Trend: As the number of carbon atoms increases, the number of isomers grows exponentially. For example, C₄H₁₀ has 2 isomers, C₅H₁₂ has 3, and C₇H₁₆ has 9, reflecting the complexity of structural arrangements.
Case Study: Isomers in Petroleum Refining
Constitutional isomers of heptane play a critical role in the petroleum industry, particularly in determining the octane rating of gasoline.
Octane Rating and Branching
n-Heptane (Straight Chain): Has a low octane rating (assigned a value of 0) because it promotes unstable combustion, leading to engine knocking.
Branched Isomers (e.g., 2,2,4-Trimethylpentane): Have high octane ratings. For example, isooctane (a branched isomer of C₈H₁₈, structurally similar to heptane isomers) is assigned an octane rating of 100.
Application in Gasoline Blending: Refineries adjust the ratio of straight-chain to branched alkanes (including heptane isomers) to achieve desired octane ratings. For instance, blending n-heptane (low octane) with branched isomers improves fuel stability.
Case Study Example: A refinery produces gasoline with an octane rating of 87 by mixing 30% n-heptane with 70% branched isomers (e.g., 2-methylhexane). This balance ensures efficient combustion without engine damage.
C₇H₁₆ is the chemical formula for heptane, which is an alkane with seven carbon atoms. When you hear "constitutional isomers," it means different compounds that have the same chemical formula but different connections between the atoms — basically, they’re built differently.
For C₇H₁₆, there are nine constitutional isomers. That means there are nine different ways you can arrange the seven carbon atoms and sixteen hydrogen atoms without changing the actual formula. Some examples include:
n-heptane (the straight chain version — just seven carbons in a row)
2-methylhexane (a six-carbon chain with a one-carbon branch on the second carbon)
3-methylhexane (branch on the third carbon)
3-ethylpentane (a five-carbon chain with a two-carbon branch on the third carbon)
3,3-dimethylpentane (two branches on the third carbon)
3,4-dimethylpentane (one branch on the third carbon, one on the fourth), and so on.
Each of these isomers has slightly different physical properties, like boiling points and densities, even though they're made of the same types of atoms.
So, long story short: C₇H₁₆ has nine constitutional isomers, and they’re all just different ways of connecting the same pieces together! Pretty cool, right?
Explanation
Constitutional isomers, also known as structural isomers, are compounds that have the same molecular formula but different connectivity of atoms. To determine the number of constitutional isomers of C₇H₁₆, we need to consider all the possible ways in which the seven carbon atoms can be connected.
The simplest isomer is n-heptane, where the seven carbon atoms are arranged in a straight chain. The other isomers include various branched structures. For example, 2-methylhexane has a six - carbon chain with a methyl group attached to the second carbon atom. 3 - methylhexane has the methyl group attached to the third carbon atom of the hexane chain.
As the branching becomes more complex, we get isomers like 2,2 - dimethylpentane, 2,3 - dimethylpentane, 2,4 - dimethylpentane, 3,3 - dimethylpentane, 3 - ethylpentane, and 2,2,3 - trimethylbutane.
Reason
The reason for the specific number of constitutional isomers is based on the principles of combinatorics and the rules of carbon - carbon bonding. Each carbon atom can form four bonds, and the carbon skeleton can be arranged in different ways to accommodate the seven carbon atoms.
The straight - chain structure is the simplest, but as we introduce branches, the number of possible arrangements increases. The more branches we have, the more ways we can distribute the carbon atoms, leading to a greater number of isomers.
Case Study: Application in the Chemical Industry
In the chemical industry, constitutional isomers of C₇H₁₆ have different applications. For example, n - heptane is often used as a standard reference fuel in octane rating tests for gasoline. Its consistent combustion properties make it an ideal candidate for this purpose.
The branched isomers, on the other hand, have different physical and chemical properties. Some of them may have higher octane ratings, making them valuable in gasoline formulations to improve engine performance and reduce knocking.
In the production of solvents, some of the isomers may be used due to their specific solubility and volatility characteristics. For instance, certain branched isomers may be better solvents for certain organic compounds.
Precautions During Operation or Use
When handling C₇H₁₆ and its isomers, safety precautions must be taken. Firstly, as hydrocarbons, they are flammable. Adequate ventilation should be provided to prevent the accumulation of vapors, and open flames or sparks should be avoided in the storage and handling areas.
Protective equipment such as gloves and safety glasses should be worn to prevent skin and eye contact. In case of spills, proper cleanup procedures should be followed to minimize environmental contamination.
In industrial settings, it is important to monitor the quality and purity of the isomers used. Impurities can affect the performance and safety of the products in which they are used.