Are there specific physical or chemical processes involved? What factors in water, like temperature or salinity, can affect the amount of dissolved oxygen? Also, how do we accurately measure dissolved oxygen levels? And what role does dissolved oxygen play in aquatic ecosystems, for example, in supporting the life of fish and other organisms?
What Do We Mean by Dissolved Oxygen in Water: The Connection of Oxygen and Dissolution?
Related Encyclopedia
Related Products More >
-
- 9003-05-8
- USD 30.0000
- 25kg
-
- 9003-05-8
- USD 30.0000
- 25kg
-
- 1336-21-6
- CNY 500.0000
- 1ton


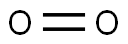
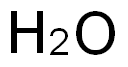

 沪ICP备2021018848号-5
沪ICP备2021018848号-5

Now, about the factors that can affect the amount of dissolved oxygen in water. Temperature is a huge one. When the water is colder, it can hold more oxygen. Think of it like a sponge. A cold sponge can absorb more water than a warm one. So, in winter or in deep, cold parts of a lake, you'll usually find higher levels of dissolved oxygen. On the other hand, as the water warms up, like in the summer or in shallow, sun - heated ponds, the water can't hold as much oxygen, and some of it escapes back into the air. Salinity also plays a role. Saltier water has less room for oxygen molecules because the salt ions take up some space. So, in the ocean where the salinity is relatively high, the dissolved oxygen levels are generally lower compared to freshwater, all other things being equal.
Measuring dissolved oxygen levels accurately is really important. One common way is with a dissolved oxygen meter. It has a special probe that you put into the water. The probe has a membrane that allows oxygen to pass through, and then it measures the electrical current generated by a chemical reaction involving the oxygen. This current is then converted into a measurement of dissolved oxygen concentration. Another method is the Winkler method, which is a chemical titration. You add some chemicals to a water sample. These chemicals react with the dissolved oxygen in the water, and then you can calculate the amount of dissolved oxygen based on how much of another chemical you need to add to make the reaction complete.
Dissolved oxygen plays a super - crucial role in aquatic ecosystems. For fish, it's like air is to us. They breathe in water through their gills, and the gills extract the dissolved oxygen from the water and release carbon dioxide. Without enough dissolved oxygen, fish can suffocate. It's not just fish, though. All sorts of aquatic organisms, like insects, crustaceans, and even plants that live underwater, need dissolved oxygen. Aquatic plants use oxygen at night for respiration, just like we do. And many bacteria in the water need oxygen to break down organic matter. If the dissolved oxygen levels drop too low, it can lead to a dead zone in the water where nothing can survive. So, maintaining good dissolved oxygen levels is key to keeping our water bodies healthy and full of life.
Temperature is a big one. Cold water can hold more dissolved oxygen than warm water. That's because as water warms up, the water molecules move around more and push the oxygen molecules out. Salinity also plays a role. Saltwater can hold less dissolved oxygen than freshwater because the salt ions get in the way of the oxygen molecules dissolving.
To accurately measure dissolved oxygen levels, we use special instruments called dissolved oxygen meters. They work by either measuring the electrical current produced when oxygen reacts with a metal electrode or by shining light through the water and measuring how much light is absorbed by the oxygen molecules.
Now, dissolved oxygen is super important in aquatic ecosystems. It's what fish and other aquatic organisms need to breathe. Without enough dissolved oxygen, they can suffocate. It's like how we need air to breathe – they need dissolved oxygen in the water. A healthy aquatic ecosystem will have plenty of dissolved oxygen to support all the different organisms living there. So, keeping an eye on dissolved oxygen levels is crucial for making sure our lakes, rivers, and oceans stay healthy and full of life.
Now, factors like temperature and salinity can really mess with how much oxygen water can hold. Cold water can hold more oxygen than warm water, which is why fish in warmer climates might struggle more with low oxygen levels. Salinity, or how salty the water is, also plays a role. Freshwater can hold more oxygen than saltwater, so if you’re in the ocean, there’s naturally less oxygen available. Other things like altitude and pressure can affect it too—higher altitudes mean less oxygen in the water because there’s less atmospheric pressure pushing it in.
Measuring dissolved oxygen is pretty straightforward these days. You can use a device called a dissolved oxygen meter, which has a probe you stick in the water, and it gives you a reading. There’s also the old-school method called the Winkler titration, where you take a water sample and add chemicals to figure out how much oxygen is in it. Both methods work, but the meter is quicker and easier if you’re out in the field.
Now, why does dissolved oxygen matter so much? Well, it’s literally life support for aquatic ecosystems. Fish, insects, and other organisms need oxygen to survive, just like we do. If oxygen levels drop too low, you get what’s called hypoxia, and that can kill off fish and other creatures. It can also mess up the whole food chain—if the small organisms die, the bigger ones that eat them starve. Plus, low oxygen can lead to things like algal blooms, where too much algae grows and then dies, using up even more oxygen as it decomposes. It’s a vicious cycle.
So yeah, dissolved oxygen is super important for keeping aquatic ecosystems healthy. It affects everything from the tiniest bacteria to the biggest fish, and without enough of it, things can go south real fast. That’s why scientists and environmentalists keep a close eye on oxygen levels in lakes, rivers, and oceans—it’s a key indicator of how healthy the water is.